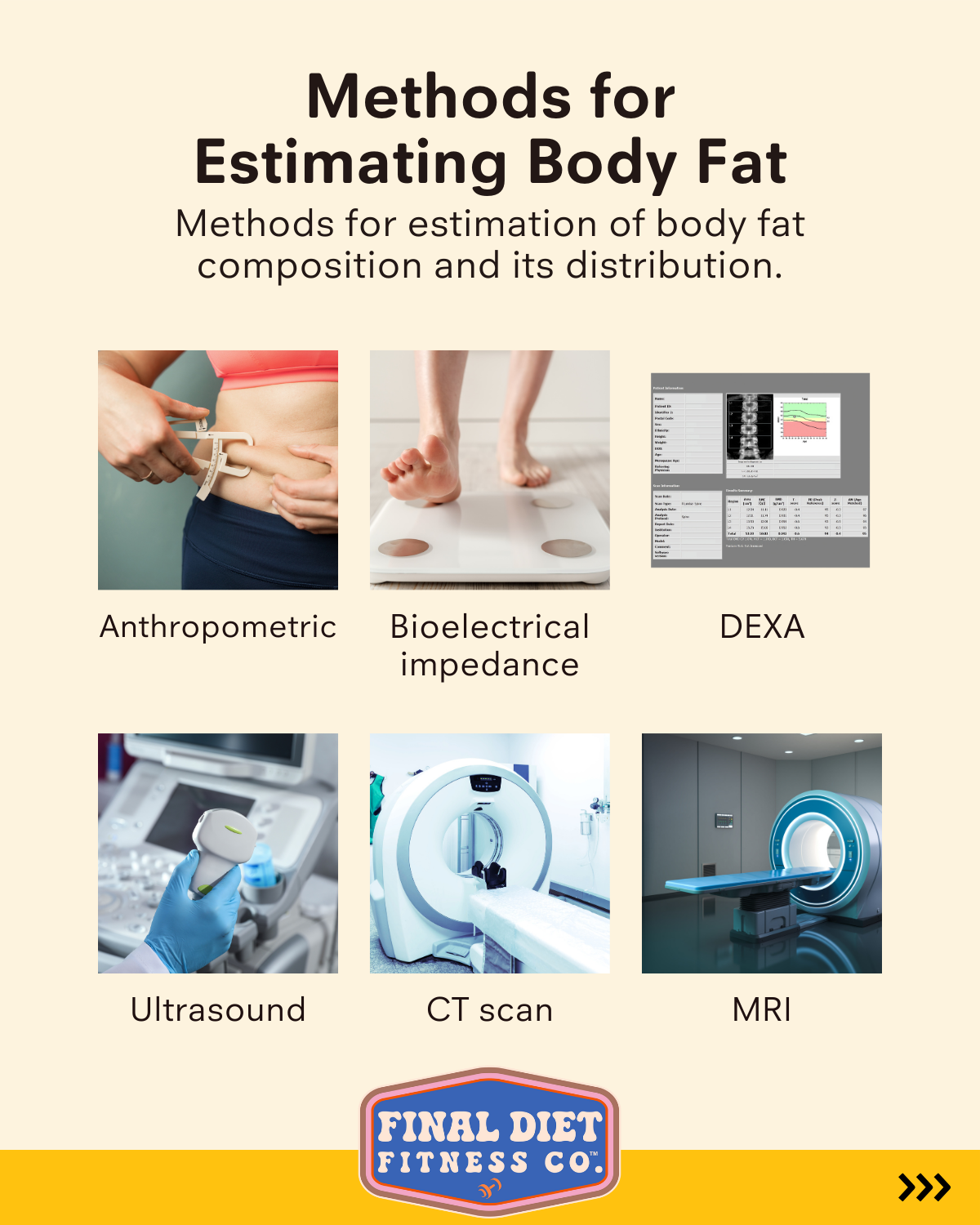
When it comes to understanding your body fat percentage, there are several methods available, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Whether you’re tracking your fitness progress or looking to assess your health, it’s essential to know which body fat estimation method works best for your needs. Below are some of the most common techniques for measuring body fat:
1. Anthropometric Measurements
Anthropometric methods involve simple measurements, such as body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio, waist circumference, arm circumference, and skinfold thickness. These measurements are typically taken manually using a tape measure or calipers.
Benefits:
- Low-Cost: These methods are affordable and easy to perform.
- Easy to Measure: Measurements can be taken at home or in any fitness setting without the need for expensive equipment.
Drawbacks:
- Accuracy: These methods may not be fully accurate and can vary depending on the technique used.
- Ethnic Differences: Body fat distribution differs across ethnic groups, which may limit the accuracy of some measurements, like BMI.
2. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
DEXA is a medical imaging technique that uses two X-ray energies to assess body composition, including fat, lean mass, and bone density.
Benefits:
- Highly Accurate: It provides a precise measurement of body fat and bone density.
- Whole-Body Assessment: DEXA scans analyze the entire body and offer a clear breakdown of fat distribution.
Drawbacks:
- Exposure to Radiation: Although the radiation dose is minimal, it is still a concern for some.
- Cost: DEXA scans can be relatively expensive compared to simpler methods.
3. Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to measure body fat by assessing the reflection of the waves as they pass through different tissues.
Benefits:
- No Radiation: Unlike X-ray methods, ultrasound is completely safe with no exposure to radiation.
- High Accuracy: Ultrasound can provide accurate measurements if performed correctly.
Drawbacks:
- User Skill: The accuracy of ultrasound depends on the skill of the operator, making it less reliable if not done correctly.
- Lack of Standardization: Different ultrasound machines may yield varying results, and there are no universal standards for body fat measurements.
4. CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
CT scans use X-ray beams and specialized digital detectors to create cross-sectional images of the body. This technology is particularly effective at analyzing body adipose tissue and other body tissues.
Benefits:
- Highly Accurate: CT scans provide detailed, whole-body assessments with precision.
- Detailed Cross-Sectional Images: Ideal for measuring fat distribution and body composition in specific areas.
Drawbacks:
- High Radiation Exposure: The radiation exposure from CT scans is higher than other methods.
- Cost: CT scans can be expensive and may not be accessible for regular use.
5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI uses strong magnets to align body protons and create detailed images of the body's internal structures. MRI is excellent for differentiating between soft tissues like fat and muscles.
Benefits:
- Excellent Soft Tissue Contrast: MRI provides clear, detailed images and is very accurate when assessing fat distribution and body composition.
- Whole-Body Assessment: Like CT scans, MRIs analyze the entire body.
Drawbacks:
- Costly: MRI scans are expensive and may not be available to everyone.
- Slower Process: MRIs take longer than CT scans and ultrasound, making them less convenient for quick assessments.
6. Bioelectrical Impedance
Bioelectrical impedance works by sending a small, harmless electrical current through the body. The rate at which the current flows is measured, and variations are used to estimate body composition, including fat mass.
Benefits:
- Low-Cost: This method is inexpensive and widely available in home scales and fitness centers.
- Convenient: Bioelectrical impedance is quick and non-invasive.
Drawbacks:
- Limited Accuracy: Factors like hydration levels, food intake, and time of day can affect the accuracy of bioelectrical impedance measurements.
Which Method is Right for You?
Each body fat measurement method has its advantages and limitations. If you’re looking for a quick and low-cost solution, anthropometric measurements or bioelectrical impedance may be your best bet. For more accuracy in tracking body composition, DEXA, MRI, or CT scans provide detailed, reliable assessments but come with higher costs. Always consult with a healthcare or fitness professional to determine which method is best for your specific needs.